Anonymous FTP
In early ages of the internet, a easy way of sharing files between user is the FTP server.
Anonymous FTP allow users to log as “Anonymous”
1999 First Generation P2P: NAPSTER
A centralized server host all the INDEXES of the different files.
-> Because of this centralize aspect the NAPSTER infrastructure was shutdown.
Second Generation P2P: GNUTELLA
Gnutella was the second major P2P network that emerged. After Napster’s demise, the creators of Gnutella wanted to create a de-centralized network — one that could not be shut down by simply turning off a server.[1]
Third Generation P2P: FASTRACK
Fasttrack is perhaps the most famous of this generation of networks.[1]
Clients: Kazaa, or Grokster or Morpheus.
Architecture overview: “The FastTrack protocol classifies some nodes as super nodes. These nodes act as directory servers for other clients and are elected without centralized control. It is certainly possible that more roles exist. There is probably some kind of aggregation between the super nodes as well, but this has not been proven. Attempts at cracking the FastTrack protocol have been made but has failed to break the encryption.” [5]
BitTorrent is a way to transfer files of just about any size quickly and efficiently. It works by breaking files up into small pieces. The file is downloaded piece by piece from one or many different sources. It’s efficient because you get faster downloads using a lot less bandwidth. The name BitTorrent is also used to describe the official BitTorrent client.[4]
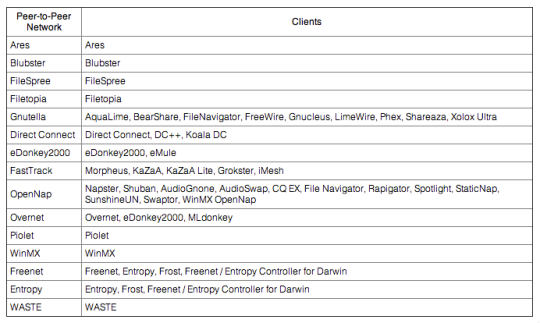
Protocol List
Reference
[1] http://www.mac-p2p.com/p2p-history/
[2] http://www.zdnet.com/topics/kazaa
[3] http://www.umkc.edu/is/security/p2p_explanation.asp?text=large
[4] http://www.bittorrent.com/help/faq/concepts
[5] http://www8.cs.umu.se/~bergner/thesis/html/node64.html




Leave a comment